|
|
5 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| contrib | 8 years ago | |
| doc | 6 years ago | |
| examples | 5 years ago | |
| src | 5 years ago | |
| test | 5 years ago | |
| .gitignore | 6 years ago | |
| LICENSE | 10 years ago | |
| README.md | 8 years ago | |
| build.sla | 5 years ago | |
README.md
ScriptForm
A stand-alone webserver that automatically generates forms from JSON to serve as frontends to scripts.
ScriptForm takes a JSON file which contains form definitions. It then constructs web forms from this JSON and serves these to users over HTTP. The user can select a form and fill it out. When the user submits the form, it is validated and the associated script is called. Data entered in the form is passed to the script through the environment.
Packages are available for:
Features
- Very rapidly construct forms with backends.
- Completely standalone HTTP server; only requires Python.
- Callbacks to any kind of script / program that supports environment variables.
- User authentication support through Basic HTAuth.
- Validates form values before calling scripts.
- Uploaded files are automatically saved to temporary files, which are passed on to the callback.
- Multiple forms in a single JSON definition file.
- Scripts can produce normal output, HTML output or stream their own HTTP response to the client. The last one lets you stream images or binaries to the browser.
- Run scripts as different users without requiring sudo.
- Audit log: All form submissions including entered values can be logged to a logfile for auditing.
Use-cases
Scriptform is very flexible and as such serves many use-cases. Most of these revolve around giving non-technical users a user friendly way to safely run scripts on a server.
Here are some of the potential uses of Scriptform:
- Add / remove users from htpasswd files.
- Execute SQL snippets.
- View service status
- Upload data to be processed.
- Restart, enable and disable services.
- Trigger for batch processing.
Example
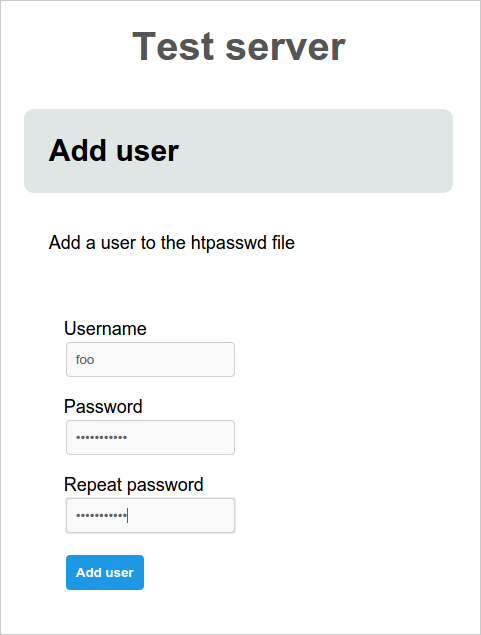
The following example lets you add new users to a htpasswd file via ScriptForm.
It presents the user with a form to enter the user's details. When the form is
submitted, the job_add_user.sh script is called which adds the user to the
htpasswd file.
Form configuration file: test_server.json
{
"title": "Test server",
"forms": [
{
"name": "add_user",
"title": "Add user",
"description": "Add a user to the htpasswd file",
"submit_title": "Add user",
"script": "job_add_user.sh",
"fields": [
{"name": "username", "title": "Username", "type": "string"},
{"name": "password1", "title": "Password", "type": "password"},
{"name": "password2", "title": "Repeat password", "type": "password"}
]
}
]
}
The script job_add_user.sh:
#!/bin/sh
if [ -z "$password1" ]; then
echo "Empty password specified" >&2; exit 1
fi
if [ "$password1" != "$password2" ]; then
echo "Passwords do not match" >&2; exit 1
fi
htpasswd -s -b .htpasswd "$username" "$password1" || exit $?
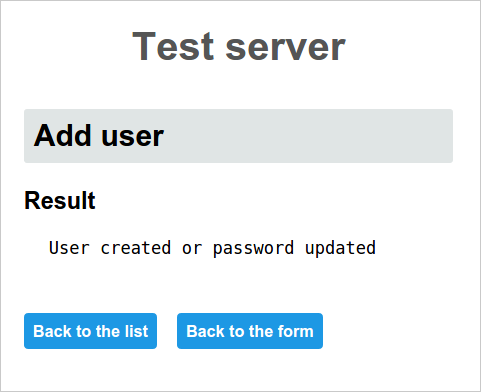
echo "User created or password updated"
Set some rights and create the initial htpasswd file:
$ chmod 755 job_add_user.sh
$ touch .htpasswd
We can now start ScriptForm to start serving the form over HTTP. By default it
starts as a daemon, so we specify the -f option to start it in the foreground
instead. We also specify the port, even though 8081 is already the default.
$ scriptform -f -p8081 ./test_server.json
The user is presented with the following form:
When submitting the form, the results are displayed.
For more examples, see the examples directory
For more screenshots, see the screenshots Wiki page
Installation
Requirements
ScriptForm requires:
- Python 2.6+
No other libraries are required. Python v2.6+ is generally available by default on almost every major linux distribution. For other platforms Python is almost certainly available.
Installation
Get the package for your operating system from the Github releases page.
For Debian / Ubuntu systems:
sudo dpkg -i scriptform*.deb
For Redhat / Centos systems:
sudo yum install scriptform*.rpm
For Other systems:
tar -vxzf scriptform*.tar.gz
cd scriptform*
sudo make install
Configuration
Scriptform provides init scripts to automatically start Scriptform at boot
time. These are not installed by default. You can find init scripts for
Debian / Ubuntu at /usr/share/doc/scriptform/scriptform.init.d_debian and
for Redhat / Centos at /usr/share/doc/scriptform/scriptform.init.d_debian.
NOTE: If you use an init script, Scriptform will run as user root, which
will cause Scriptform to automatically drop privileges to user nobody and
group nobody when executing shell scripts. This may cause "permission
denied" problems! See the "Execution security policy" chapter in the User
Manual for more information.
To install the init script:
For Debian / Ubuntu systems:
sudo cp /usr/share/doc/scriptform/scriptform.init.d_debian /etc/init.d/scriptform
sudo chmod 755 /etc/init.d/scriptform
sudo update-rc.d scriptform defaults
Then edit /etc/init.d/scriptform and change the FORM_CONFIG setting to
point at the form configuration JSON file you'd like to use.
For RedHat / Centos systems:
sudo cp /usr/share/doc/scriptform/scriptform.init.d_redhat /etc/init.d/scriptform
sudo chmod 755 /etc/init.d/scriptform
sudo chkconfig --add scriptform
sudo chkconfig scriptform on
Then edit /etc/init.d/scriptform and change the FORM_CONFIG setting to
point at the form configuration JSON file you'd like to use.
There's also a Systemd unit file, which should work on most systems that run on systemd:
sudo cp /usr/share/doc/scriptform/scriptform.service /etc/systemd/system/
Then edit /etc/systemd/system/scriptform.service and make change the
FORM_CONFIG environment variable to point at the form configuration JSON
file you'd like to use.
Usage
Usage:
Usage: /usr/bin/scriptform [option] (--start|--stop) <form_definition.json>
/usr/bin/scriptform --generate-pw
Options:
--version show program's version number and exit
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-g, --generate-pw Generate password
-p PORT, --port=PORT Port to listen on (default=8081)
-f, --foreground Run in foreground (debugging)
-r, --reload Reload form config on every request (DEV)
--pid-file=PID_FILE Pid file
--log-file=LOG_FILE Log file
--start Start daemon
--stop Stop daemon
ScriptForm can run both in daemon mode or in the foreground. In daemon mode, we
can control ScriptForm with the --start and --stop options. By default it
runs on port 8081, which we can change with the -p option.
$ scriptform -p8081 ./test_server.json
This puts ScriptForm in the background as a daemon. It creates a PID file and a log file.
$ tail scriptform.log
2015-04-08 07:57:27,160:DAEMON:INFO:Starting
2015-04-08 07:57:27,161:DAEMON:INFO:PID = 5614
2015-04-08 07:57:27,162:SCRIPTFORM:INFO:Listening on 0.0.0.0:8081
In order to stop the daemon:
$ scriptform --stop
We can control the location of the PID file and log file with the --pid-file
and --log-file options. If we don't specify these, ScriptForm will create
them in the local directory.
To run ScriptForm in the foreground, specify the -f option.
If you're going to use built-in basic authentication, you can generate a
password for your user with the --generate-pw option:
$ scriptform --generate-pw
Password:
Repeat password:
2c26b46b68ffc68ff99b453c1d30413413422d706483bfa0f98a5e886266e7ae
You can paste the generated password into the password field. You can also use an Apache (or other webserver) frontend for authentication. For more information, see the User Manual.
Documentation
The User Manual is the main source for all your documentation needs:
- Read the tutorial to quickly get aquinted with Scriptform.
- Read about form configurations to learn all the configuration options for Scriptform and your forms.
- The field types chapter lists all the possible fields and which options they take.
Security
ScriptForm is only as secure as you write your scripts. Although form values are validated before calling scripts, many possible security problems should be taken into consideration. As such, you should never expose ScriptForm to the public internet. Its intended end users should be people you trust at least to a certain degree.
License
ScriptForm is released under the following license:
GPLv3 license.
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.